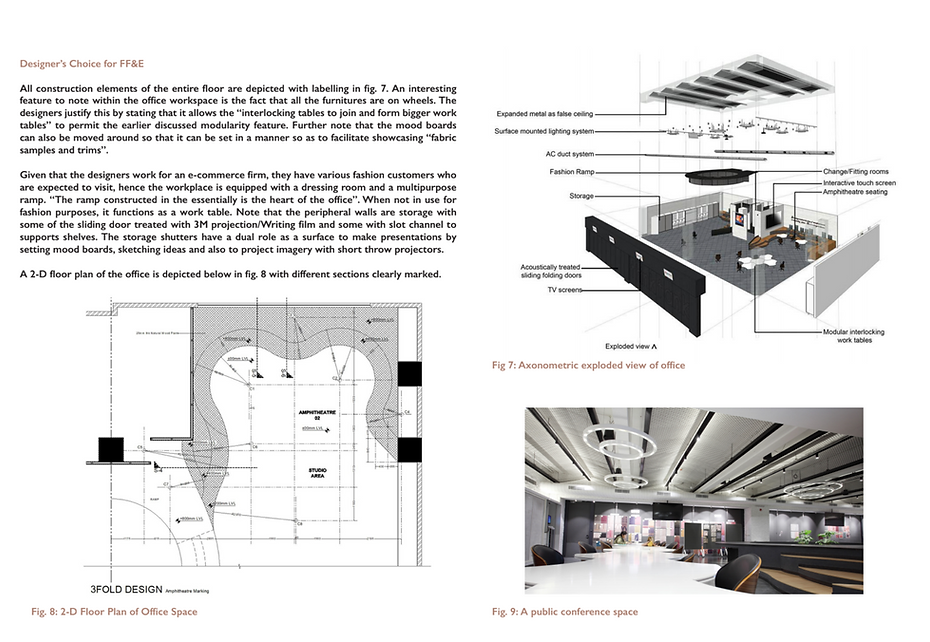
Literature Review
Literature review 1
—
This proposal aims to address the detrimental health impacts of sedentary activity among desk job workers in the information technology (IT) sector due to poor office ergonomics and high work pressure in the city of Bangalore, the IT capital of India. The following literature review consists of a collection of journal articles that explores physical, social, psychological and cultural factors that are responsible for musculoskeletal disorders and mental stress among computer professionals in Bangalore. The chosen articles collectively provide adequate background on the current situation of IT workers in Bangalore to make informed decisions for the proposal. Gaps in research revolve around the description of office spaces in IT companies in Bangalore. Nevertheless, these gaps can be filled by conducting precedent studies and primary research in the near future.
Physical Factor. The first source is a journal paper titled “Prevalence of complaints of arm, neck and shoulders among computer professionals in Bangalore: A cross sectional study” by authors Vijay Mohan, Leeberk R. Inbaraj, Carolin E. George, and Gift Norman. The article discusses a cross sectional study conducted in Bangalore by the Department of Family Medicine and Community Health to evaluate the reasons behind Complaints of arm, neck, and shoulders (CANS) among computer professionals. The study was conducted by asking workers in various IT companies in Bangalore to fill out questionnaires which were then put through statistical analysis. It was found that 58.6% of the study group reported CANS. Furthermore, two of the primary reasons behind CANS were found to be lack of space and redundancy of job tasks. The article concludes by highlighting that CANS is ‘highly prevalent’ among IT desk job workers in Bangalore, specifically in small - medium range companies. The authors stress on the need to improve workspace and ergonomic conditions of the offices of such companies. Furthermore, the authors emphasize on the need for better work habits and posture correction. This article is highly useful firstly as it was published recently, in 2019, which shows the relevancy and urgency of the problem. Secondly, the authors provide numerous reasons for the existence of the problem. The paper addresses several physical factors in the workplace that are leading causes to musculoskeletal problems in the body and this provides a scope for the proposal to aim to achieve by mitigating such physical discomforts.
Literature review 2
—
Physiological Factor. The third source is a journal paper titled
“Work-Related Musculoskeletal Injury Risk Assessment and its Relevance to Body Mass Index for Computer Professionals” by Prasanna Mohan, S.G. Sudhan, Kannan Dhasaradharaman, and Anjali Suresh. In this journal article, researchers from the Department of Physiotherapy at Garden City University in Bangalore aim to corelate the Body Mass Index of 142 IT employees from medium-large companies to musculoskeletal pain. Although the primary focus of this article is to draw a relation between the height and weight of employees to occurrence of work-related pain, the article also provides an insight into various psychological and physical factors that trigger the pain. The article discusses how more movement within the workplace can improve the quality of workstyle.
This is established as opposed to several participants who reported long hours of sitting in the same posture leading to reduced quality of workstyle. The article highlights how the lack of knowledge among employees regarding their own work atmosphere due to a complex compact setting or layout of the elements in the office is one of the causes for the longer time spent sitting. This particular point raised by the authors is very useful to not making the design proposal overly complicated. It can be inferred from the article that the workspace should be simplistic nature so that it can be easily understood and comfortably accessed.
Literature review 3
—
The literature review that has been conducted above gathers a substantial amount of background needed to address the adverse health impacts of sedentary activity among desk job workers in the information technology sector in Bangalore. The four articles together discuss four major factors – physical, social, psychological and cultural – that are leading causes to musculoskeletal pain and high work pressure among computer professionals in Bangalore. Some of the major physical factors that have been raised in these articles include bad posture and poor ergonomics.
The social factors addressed in these articles mainly pertain to social inactivity. The psychological factors involve high work pressure. Finally, the major cultural factor in Bangalore is that of fear among workers of being pushed out of their jobs. Note that these articles do not entirely fill gaps in research surrounding description of workplaces and elements of poor ergonomics in the office. This, however, will be done through precedent studies and primary research later. The collection of articles, nevertheless, would largely influence the design proposal of a space for desk-job IT workers in Bangalore.
—
Social Factor. The second source is a journal paper titled “Workstyle Risk Factors for Work Related Musculoskeletal Symptoms Among Computer Professionals in India” by Deepak Sharan, Prakriti Parijat, Ajeesh P. Sasidharan, Rameshkumar Ranganathan, Mathankumar Mohandoss, and Jeena Jose. In this journal article, researchers from the Neuromusculoskeletal Rehabilitation Centre in Bangalore aim to corelate poor workstyle to loss in productivity among computer professionals in IT companies.
The method followed by the researchers is similar to that in the first article, where 4500 employees from IT companies in Bangalore were asked to fill out questionnaires regarding their work life and the results were put through statistical analysis. It was found that 63% of the participants reported having symptoms of Musculoskeletal pain. Three major factors were found to be leading causes to the pain faced by the study group – social inactivity, fewer breaks, and the constant pressure of dealing with deadlines. Furthermore, the article also mentions how musculoskeletal pain can lead to physiological problems in the body such as high blood pressure and weaker muscles and that the problem is indeed of high importance making it imperative to be addressed. This article is extremely useful as it identifies social factors that lead to musculoskeletal pain. This enables to add a social aspect to the design proposal, hence giving it more depth. The design could consider promoting social interaction and activity among employees.
—
Cultural Factor. The fourth source is a journal article titled “Occupational Stress among Information Technology Professionals in India: A Systematic Review of Literature” by B.Prathyusha. Some of the key matters that this journal article brings to attention are the cultural and psychological factors that explain why mental stress is prevalent particularly among IT workers in Bangalore. The article makes sure to firstly establish that ‘Workplace stress’. The article discusses work exhaustion faced by IT workers in Bangalore. The author mentions that one the major causes for high mental pressure among computer professionals in Bangalore is the fear of becoming outdated. Workers fear that if they don’t catch up with the latest technological trends and advances and also the intense competition in the IT sector in India, then their work would no longer be needed.
Hence, they feel the need to constantly push themselves. However, this comes at the cost of their health. Furthermore, the article also addresses how high mental pressure at work leads to decline in job satisfaction which further results in depression and other psychological disorders. This article is extremely beneficial for the proposal as it shows why the issue is localized in the city of Bangalore. It further provides a psychological aspect to the proposal that can motivate certain design decisions that aim to make employees happier about their work environment.
—
The literature review that has been conducted above gathers a substantial amount of background needed to address the adverse health impacts of sedentary activity among desk job workers in the information technology sector in Bangalore. The four articles together discuss four major factors – physical, social, psychological and cultural – that are leading causes to musculoskeletal pain and high work pressure among computer professionals in Bangalore. Some of the major physical factors that have been raised in these articles include bad posture and poor ergonomics. The social factors addressed in these articles mainly pertain to social inactivity.
The psychological factors involve high work pressure. Finally, the major cultural factor in Bangalore is that of fear among workers of being pushed out of their jobs. Note that these articles do not entirely fill gaps in research surrounding description of workplaces and elements of poor ergonomics in the office. This, however, will be done through precedent studies and primary research later. The collection of articles, nevertheless, would largely influence the design proposal of a space for desk-job IT workers in Bangalore.